 |
| March 05, 2024 | Volume 20 Issue 09 |
Mechanical News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
New 'breathable' rupture disk tech provides overpressure and vacuum relief
 To increase equipment safety and reliability, a new rupture disk technology activates at a set burst pressure, but it can also "breathe" to relieve minor pressure fluctuations. The patent-pending, dual-function device from BS&B Safety Systems is ideal for use on low-pressure vessels that are susceptible to ambient temperature changes.
To increase equipment safety and reliability, a new rupture disk technology activates at a set burst pressure, but it can also "breathe" to relieve minor pressure fluctuations. The patent-pending, dual-function device from BS&B Safety Systems is ideal for use on low-pressure vessels that are susceptible to ambient temperature changes.
Read the full article.
Engineer's Toolbox: 9 considerations for specifying a slewing ring bearing
 In applications that require a bearing to support a structure while it rotates (e.g., cranes, radar, tank turrets), premature bearing failure can put people and equipment at risk. While slewing ring bearings have proven themselves countless times in such applications, designers must consider many factors when specifying them. According to engineers at Kaydon, the bearing's support structure, mounting (including bolt strength, tensioning, and hole patterns), installation, and even storage are all factors in a bearing's success or failure.
In applications that require a bearing to support a structure while it rotates (e.g., cranes, radar, tank turrets), premature bearing failure can put people and equipment at risk. While slewing ring bearings have proven themselves countless times in such applications, designers must consider many factors when specifying them. According to engineers at Kaydon, the bearing's support structure, mounting (including bolt strength, tensioning, and hole patterns), installation, and even storage are all factors in a bearing's success or failure.
Read the full article.
ClampDisk micro fastener is new alternative for automotive and consumer electronics
 Designed as a unique alternative in assemblies for the automotive and consumer electronics markets, the ClampDisk Press-on Fastener is a new offering from PennEngineering that delivers a fast, simple way to achieve sheet-to-sheet clamped fastening while replacing the use of standard screws, nuts, and adhesives. The most common challenges that can be eliminated or reduced by using ClampDisk include over installation, cross threading, stripped screw heads, broken screws, and damaged product. This fastener can be removed easily with a sharp-edged tool.
Designed as a unique alternative in assemblies for the automotive and consumer electronics markets, the ClampDisk Press-on Fastener is a new offering from PennEngineering that delivers a fast, simple way to achieve sheet-to-sheet clamped fastening while replacing the use of standard screws, nuts, and adhesives. The most common challenges that can be eliminated or reduced by using ClampDisk include over installation, cross threading, stripped screw heads, broken screws, and damaged product. This fastener can be removed easily with a sharp-edged tool.
Learn more and see how ClampDisk works.
New nylon constant torque hinge
 Southco has expanded its line of E6 Constant Torque Hinges with a compact, nylon version designed for small applications. The newest addition to the company's E6 50 Constant Torque Position Control Hinge series measures 45 mm with a torque range of 4 to 16 in./lb and is 65% lighter compared to the standard E6 50 Hinge. It provides constant resistance throughout the entire range of motion, enabling users to easily position doors, display screens, and other mounted components and hold them securely at any desired angle.
Southco has expanded its line of E6 Constant Torque Hinges with a compact, nylon version designed for small applications. The newest addition to the company's E6 50 Constant Torque Position Control Hinge series measures 45 mm with a torque range of 4 to 16 in./lb and is 65% lighter compared to the standard E6 50 Hinge. It provides constant resistance throughout the entire range of motion, enabling users to easily position doors, display screens, and other mounted components and hold them securely at any desired angle.
Learn more.
What injection molding material do I use?
 How do you decide what type of plastic to use for your next injection molding project? Xometry can help you narrow your choices. Discover the different strengths and applications for materials that could be ideal for your application by learning about the most common plastic injection molding materials in detail.
How do you decide what type of plastic to use for your next injection molding project? Xometry can help you narrow your choices. Discover the different strengths and applications for materials that could be ideal for your application by learning about the most common plastic injection molding materials in detail.
Read this detailed Xometry article.
What are carbon composite bellows springs?
 The Carbon Composite Bellows Spring (CCBS) from MW Components is a system of carbon fiber elements that combine to work as a high-performance, lightweight, and design-flexible compression spring meant to replace coil springs or metallic Belleville disc springs. A functional spring is made from several individual elements paired and joined to make a stack. The stack spring rate is determined by the number of elements, the base rate of each element, and their series or parallel orientation in the stack. Applications include motorsports, aerospace, and high-performance activities.
The Carbon Composite Bellows Spring (CCBS) from MW Components is a system of carbon fiber elements that combine to work as a high-performance, lightweight, and design-flexible compression spring meant to replace coil springs or metallic Belleville disc springs. A functional spring is made from several individual elements paired and joined to make a stack. The stack spring rate is determined by the number of elements, the base rate of each element, and their series or parallel orientation in the stack. Applications include motorsports, aerospace, and high-performance activities.
Learn more.
Conductive Brush Ring overcomes current leakage in EV powertrains
 SKF's new Conductive Brush Ring paves the way to greater reliability and longer life in high-performance electric vehicle powertrain systems. Using pure carbon fiber bristles, it provides a reliable electrical connection between an EV eAxle rotor shaft and its housing. When used in combination with SKF Hybrid ceramic ball bearings, it helps to alleviate parasitic current effects that can lead to premature failure in bearings and other components. Available in different configurations for wet (oil-lubricated) motor designs -- and soon for dry (sealed) applications.
SKF's new Conductive Brush Ring paves the way to greater reliability and longer life in high-performance electric vehicle powertrain systems. Using pure carbon fiber bristles, it provides a reliable electrical connection between an EV eAxle rotor shaft and its housing. When used in combination with SKF Hybrid ceramic ball bearings, it helps to alleviate parasitic current effects that can lead to premature failure in bearings and other components. Available in different configurations for wet (oil-lubricated) motor designs -- and soon for dry (sealed) applications.
Learn more.
hyperMILL 2024 CAD/CAM software suite
 OPEN MIND Technologies has introduced its latest hyperMILL 2024 CAD/CAM software suite, which includes a range of powerful enhancements to its core toolpath capabilities, as well as new functionality for increased NC programming efficiency in applications ranging from 2.5D machining to 5-axis milling. New and enhanced capabilities include: Optimized Deep Hole Drilling, a new algorithm for 3- and 5-axis Rest Machining, an enhanced path layout for the 3D Plane Machining cycle, better error detection, and much more.
OPEN MIND Technologies has introduced its latest hyperMILL 2024 CAD/CAM software suite, which includes a range of powerful enhancements to its core toolpath capabilities, as well as new functionality for increased NC programming efficiency in applications ranging from 2.5D machining to 5-axis milling. New and enhanced capabilities include: Optimized Deep Hole Drilling, a new algorithm for 3- and 5-axis Rest Machining, an enhanced path layout for the 3D Plane Machining cycle, better error detection, and much more.
Learn more.
One-part epoxy changes from red to clear under UV
 Master Bond UV15RCL is a low-viscosity, cationic-type UV-curing system with a special color-changing feature. The red material changes to clear once exposed to UV light, indicating that there is UV light access across the adhesive material. Although this change in color from red to clear does not indicate a full cure, it does confirm that the UV light has reached the polymer. This epoxy is an excellent electrical insulator. UV15RCL adheres well to metals, glass, ceramics, and many plastics, including acrylics and polycarbonates.
Master Bond UV15RCL is a low-viscosity, cationic-type UV-curing system with a special color-changing feature. The red material changes to clear once exposed to UV light, indicating that there is UV light access across the adhesive material. Although this change in color from red to clear does not indicate a full cure, it does confirm that the UV light has reached the polymer. This epoxy is an excellent electrical insulator. UV15RCL adheres well to metals, glass, ceramics, and many plastics, including acrylics and polycarbonates.
Learn more.
SPIROL Press-N-Lok™ Pin for plastic housings
 The Press-N-Lok™ Pin was designed to permanently retain two plastic components to each other. As the pin is inserted, the plastic backfills into the area around the two opposing barbs, resulting in maximum retention. Assembly time is quicker, and it requires lower assembly equipment costs compared to screws and adhesives -- just Press-N-Lok™!
The Press-N-Lok™ Pin was designed to permanently retain two plastic components to each other. As the pin is inserted, the plastic backfills into the area around the two opposing barbs, resulting in maximum retention. Assembly time is quicker, and it requires lower assembly equipment costs compared to screws and adhesives -- just Press-N-Lok™!
Learn more about the new Press-N-Lok™ Pin.
Why hybrid bearings are becoming the new industry standard
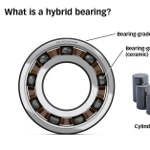 A combination of steel outer and inner rings with ceramic balls or rollers is giving hybrid bearings unique properties, making them suitable for use in a wide range of modern applications. SKF hybrid bearings make use of silicon nitride (twice as hard as bearing steel) rolling elements and are available as ball bearings, cylindrical roller bearings, and in custom designs. From electric erosion prevention to friction reduction and extended maintenance intervals, learn all about next-gen hybrid bearings.
A combination of steel outer and inner rings with ceramic balls or rollers is giving hybrid bearings unique properties, making them suitable for use in a wide range of modern applications. SKF hybrid bearings make use of silicon nitride (twice as hard as bearing steel) rolling elements and are available as ball bearings, cylindrical roller bearings, and in custom designs. From electric erosion prevention to friction reduction and extended maintenance intervals, learn all about next-gen hybrid bearings.
Read the SKF technical article.
3M and Ansys train engineers on simulating adhesives
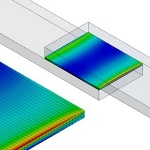 Ansys and 3M have created an advanced simulation training program enabling engineers to enhance the design and sustainability of their products when using tapes and adhesives as part of the design. Simulation enables engineers to validate engineering decisions when analyzing advanced polymeric materials -- especially when bonding components made of different materials. Understand the behavior of adhesives under real-world conditions for accurate modeling and design.
Ansys and 3M have created an advanced simulation training program enabling engineers to enhance the design and sustainability of their products when using tapes and adhesives as part of the design. Simulation enables engineers to validate engineering decisions when analyzing advanced polymeric materials -- especially when bonding components made of different materials. Understand the behavior of adhesives under real-world conditions for accurate modeling and design.
Read this informative Ansys blog.
New FATH T-slotted rail components in black from AutomationDirect
 Automation-Direct has added a wide assortment of black-colored FATH T-slotted hardware components to match their SureFrame black anodized T-slotted rails, including: cube connectors (2D and 3D) and angle connectors, joining plates of many types, brackets, and pivot joints. Also included are foot consoles, linear bearings in silver and black, cam lever brakes, and L-handle brakes. FATH T-slotted hardware components are easy to install, allow for numerous T-slotted structure configurations, and have a 1-year warranty against defects.
Automation-Direct has added a wide assortment of black-colored FATH T-slotted hardware components to match their SureFrame black anodized T-slotted rails, including: cube connectors (2D and 3D) and angle connectors, joining plates of many types, brackets, and pivot joints. Also included are foot consoles, linear bearings in silver and black, cam lever brakes, and L-handle brakes. FATH T-slotted hardware components are easy to install, allow for numerous T-slotted structure configurations, and have a 1-year warranty against defects.
Learn more.
Weird stuff: Moon dust simulant for 3D printing
 Crafted from a lunar regolith simulant, Basalt Moon Dust Filamet™ (not a typo) available from The Virtual Foundry closely mirrors the makeup of lunar regolith found in mare regions of the Moon. It enables users with standard fused filament fabrication (FFF) 3D printers to print with unparalleled realism. Try out your ideas before you go for that big space contract, or help your kid get an A on that special science project.
Crafted from a lunar regolith simulant, Basalt Moon Dust Filamet™ (not a typo) available from The Virtual Foundry closely mirrors the makeup of lunar regolith found in mare regions of the Moon. It enables users with standard fused filament fabrication (FFF) 3D printers to print with unparalleled realism. Try out your ideas before you go for that big space contract, or help your kid get an A on that special science project.
Learn more.
Break the mold with custom injection molding by Rogan
 With 90 years of industry experience, Rogan Corporation possesses the expertise to deliver custom injection molding solutions that set businesses apart. As a low-cost, high-volume solution, injection molding is the most widely used plastics manufacturing process. Rogan processes include single-shot, two-shot, overmolding, and assembly. Elevate your parts with secondary operations: drilling and tapping, hot stamping, special finishes, punch press, gluing, painting, and more.
With 90 years of industry experience, Rogan Corporation possesses the expertise to deliver custom injection molding solutions that set businesses apart. As a low-cost, high-volume solution, injection molding is the most widely used plastics manufacturing process. Rogan processes include single-shot, two-shot, overmolding, and assembly. Elevate your parts with secondary operations: drilling and tapping, hot stamping, special finishes, punch press, gluing, painting, and more.
Learn more.
Researchers boost common catalytic reactions with just a little electricity
Applying a small voltage to a catalyst can increase the rates of reactions used in petrochemical processing, pharmaceutical manufacture, and many other processes.
By David L. Chandler, MIT
A simple technique that uses small amounts of energy could boost the efficiency of some key chemical processing reactions by up to a factor of 100,000, MIT researchers report. These reactions are at the heart of petrochemical processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and many other industrial chemical processes.
The surprising findings are reported in the journal Science, in a paper by MIT graduate student Karl Westendorff, professors Yogesh Surendranath and Yuriy Roman-Leshkov, and two others.
"The results are really striking," says Surendranath, a professor of chemistry and chemical engineering. Rate increases of that magnitude have been seen before but in a different class of catalytic reactions known as redox half-reactions, which involve the gain or loss of an electron. The dramatically increased rates reported in the new study "have never been observed for reactions that don't involve oxidation or reduction," he says.
The non-redox chemical reactions studied by the MIT team are catalyzed by acids. "If you're a first-year chemistry student, probably the first type of catalyst you learn about is an acid catalyst," Surendranath says. There are many hundreds of such acid-catalyzed reactions, "and they're super important in everything from processing petrochemical feedstocks to making commodity chemicals to doing transformations in pharmaceutical products. The list goes on and on."
"These reactions are key to making many products we use daily," adds Roman-Leshkov, a professor of chemical engineering and chemistry.
But the people who study redox half-reactions, also known as electrochemical reactions, are part of an entirely different research community than those studying non-redox chemical reactions, known as thermochemical reactions. As a result, even though the technique used in the new study, which involves applying a small external voltage, was well-known in the electrochemical research community, it had not been systematically applied to acid-catalyzed thermochemical reactions.
People working on thermochemical catalysis, Surendranath says, "usually don't consider" the role of the electrochemical potential at the catalyst surface, "and they often don't have good ways of measuring it. And what this study tells us is that relatively small changes, on the order of a few hundred millivolts, can have huge impacts -- orders of magnitude changes in the rates of catalyzed reactions at those surfaces."
"This overlooked parameter of surface potential is something we should pay a lot of attention to because it can have a really, really outsized effect," he says. "It changes the paradigm of how we think about catalysis."
Chemists traditionally think about surface catalysis based on the chemical binding energy of molecules to active sites on the surface, which influences the amount of energy needed for the reaction, he says. But the new findings show that the electrostatic environment is "equally important in defining the rate of the reaction."
The team has already filed a provisional patent application on parts of the process and is working on ways to apply the findings to specific chemical processes. Westendorff says their findings suggest that "we should design and develop different types of reactors to take advantage of this sort of strategy. And we're working right now on scaling up these systems."
While their experiments so far were done with a two-dimensional planar electrode, most industrial reactions are run in three-dimensional vessels filled with powders. Catalysts are distributed through those powders, providing a lot more surface area for the reactions to take place. "We're looking at how catalysis is currently done in industry and how we can design systems that take advantage of the already existing infrastructure," Westendorff says.
Surendranath adds that these new findings "raise tantalizing possibilities: Is this a more general phenomenon? Does electrochemical potential play a key role in other reaction classes as well? In our mind, this reshapes how we think about designing catalysts and promoting their reactivity."
Roman-Leshkov adds that "traditionally people who work in thermochemical catalysis would not associate these reactions with electrochemical processes at all. However, introducing this perspective to the community will redefine how we can integrate electrochemical characteristics into thermochemical catalysis. It will have a big impact on the community in general."
While there has typically been little interaction between electrochemical and thermochemical catalysis researchers, Surendranath says, "this study shows the community that there's really a blurring of the line between the two, and that there is a huge opportunity in cross-fertilization between these two communities."
Westerndorff adds that to make it work, "you have to design a system that's pretty unconventional to either community to isolate this effect." And that helps explain why such a dramatic effect had never been seen before. He notes that even their paper's editor asked them why this effect hadn't been reported before. The answer has to do with "how disparate those two ideologies were before this," he says. "It's not just that people don't really talk to each other. There are deep methodological differences between how the two communities conduct experiments. And this work is really, we think, a great step toward bridging the two."
In practice, the findings could lead to far more efficient production of a wide variety of chemical materials, the team says. "You get orders of magnitude changes in rate with very little energy input," Surendranath says. "That's what's amazing about it."
The findings, he says, "build a more holistic picture of how catalytic reactions at interfaces work, irrespective of whether you're going to bin them into the category of electrochemical reactions or thermochemical reactions." He adds that "it's rare that you find something that could really revise our foundational understanding of surface catalytic reactions in general. We're very excited."
Published March 2024
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy

